Within the intricate realm of the stock market, hedging is a tactical maneuver aimed at shielding an investor's portfolio – not merely to guard the accrued gains but as a crucial counterpart to portfolio growth.
Key Points on Hedging
- Hedging acts as a financial safeguard against potential investment losses by establishing a counterbalancing position in a related asset.
- The security hedging offers comes at the expense of potential higher profits and the cost of the premium for the protection.
- Predominantly, hedging strategies engage derivatives, such as options and futures, to structure this protective shield.
Exploring Hedging
Imagine hedging as insurance for your financial health. It doesn't avert misfortune but mitigates financial repercussions if misfortunes strike. Hedging is akin to insurance policies against life's uncertainties, such as a homeowner's insurance guarding against fires or theft. In the realm of portfolio management, corporate finance, and individual investments, hedging is adopted to manage exposure to various financial risks. In contrast to traditional insurance, financial market hedging is not as straightforward as paying an annual premium; it involves nuanced financial instruments and market strategies.
Hedging in Practice
To execute a hedge, an investor engages in offsetting trades within negatively correlated securities. Although this financial "insurance" comes at a cost, it's a price for reducing potential loss, not necessarily for amplifying potential gains. If the main investment prospers, hedging typically trims the upside. Conversely, if there's a loss, an effective hedge will cushion the blow.
The Mechanisms of Hedging
Derivatives such as options and futures are the linchpins of hedging. These financial instruments can be deftly wielded to set up trading strategies where gains in derivatives counterbalance losses in investments. Let's delve into an illustrative scenario: You hold shares in Cory's Tequila Corporation (ticker: CTC) and foresee potential short-term dips in the tequila market. By purchasing a put option on CTC, you gain the right to sell your shares at a pre-set price, safeguarding your investment against decline. This approach is termed a 'married put'.
Extending this example to a corporate context, consider Cory's Tequila Corporation's vulnerability to the volatile agave prices. A futures contract can lock in a purchase price for agave, thus insulating the company's financial forecast from the whims of the market. However, should the market price fall below the contracted rate, the company misses out on potential savings, highlighting the trade-off intrinsic to hedging.
The Flip Side of Hedging
Hedging is not free of drawbacks. The cost of hedging – whether it's the premium for an option or the missed opportunity for gains – cannot be sidestepped. Hedging is less about financial gain and more about loss prevention. Moreover, unlike insurance, which compensates for losses more thoroughly, hedging offers no guarantee of a perfect financial buffer due to market complexities.
Hedging's Relevance for Individual Investors
Although derivative trading may not appeal to all investors, particularly those with a 'buy-and-hold' philosophy, understanding hedging is invaluable. Major corporations and investment funds often resort to hedging. An oil company might hedge against fluctuating oil prices, or an international mutual fund against forex rate oscillations. Appreciating the mechanics of hedging enhances one's financial literacy and informs the evaluation of such hedged investments. In summary, while hedging in the forex market or any investment avenue is multifaceted and not without its costs, its inclusion in a financial strategy can serve as a bulwark against adverse market movements. Grasping the essence of hedging strategies ensures that investors, irrespective of their involvement in such practices, can navigate the investment environment with a more informed perspective.
To analyze and select the top 10 brokers suitable for forex hedging, we must consider various factors such as hedging features, trading platforms, regulatory compliance, spreads, commissions, customer service, and additional tools that may benefit a hedging strategy. The selected brokers should offer direct hedging capabilities, allowing clients to hold both buy and sell positions in the same currency pair simultaneously. It's also essential that these brokers provide a stable trading environment with competitive spreads and access to advanced trading tools.
After considering these factors, here are the top 10 brokers selected for hedging in forex, with extended overviews of their hedging features and other relevant aspects:
Understanding Hedging: Strategies for Stabilizing Financial Outcomes
The concept of a forward hedge is best illustrated through the lens of agricultural production, such as a wheat farmer's annual cycle. Consider a wheat farmer who sows his crop in the spring with the intent to harvest and sell in the fall. From the moment of planting, the farmer becomes vulnerable to fluctuations in wheat prices. By the time fall arrives, the market price could decline, potentially reducing the farmer's revenue from the sale of the wheat. Given the farmer's primary interest lies in safeguarding the profitability of his farming operations rather than speculating on wheat prices, a forward hedge serves as a critical risk management strategy.
To hedge his exposure to a potential drop in wheat prices, the farmer may engage in a forward contract at the time of planting. Let's say the current market price is $40 per bushel; the farmer enters into a six-month futures contract to sell his anticipated harvest at this price, establishing a forward hedge. When harvest time comes, assume the market price has fallen to $32 per bushel. The farmer sells his wheat at this new market rate, concurrently closing his short futures position at the same price. The transaction in the futures market yields an $8 per bushel profit, offsetting the lower sale price and effectively securing a realized price of $40 per bushel.
Alternatively, if the price of wheat had risen to $44 per bushel at the time of harvest, the farmer would benefit from selling his crop at this higher market price. However, closing the short futures position would now result in a $4 per bushel loss. Despite this, the farmer achieves a net selling price of $40 per bushel, demonstrating the hedging strategy's effectiveness in stabilizing income irrespective of price volatility.
A protective put hedge further exemplifies risk mitigation strategies in the financial markets. This technique involves purchasing a put option, which entitles but does not obligate the holder to sell a security at a predetermined price, known as the strike price. An investor holding shares of XYZ Company priced at $100 might fear a decline in value. To hedge against a potential drop of 10%, the investor could purchase a put option with a strike price of $90. Should XYZ's stock plummet to $50, the protective put allows the investor to sell at $90, minimizing the loss. In the realm of options trading, delta serves as a pivotal metric, indicating how much an option's premium is expected to change with a $1 fluctuation in the underlying asset's price. A call option with a delta of 30 suggests a $0.30 change in the premium for every $1 move in the underlying asset. To achieve delta neutrality, and thus hedge directional risk, an investor could sell 30 shares of the underlying security, given that one options contract typically represents 100 shares of stock.
Commercial hedgers, such as corporations or producers, utilize derivatives to offset their exposure to market risks related to the goods they produce or the resources they require. For example, a cereal manufacturer like Kellogg's might buy corn futures to hedge against the potential for rising corn costs. Conversely, a corn farmer could sell futures to protect against a decrease in corn prices before the crop is ready for market.
De-hedging refers to the unwinding of hedge positions, which can be strategic if the hedge is deemed unnecessary, too costly, or if the entity decides to accept the uncovered risk for a potentially greater reward. In summary, understanding risk is fundamental to investing and commercial operations. Familiarity with hedging strategies is critical for investors and companies aiming to protect their financial interests. Whether one actively employs derivatives or not, an appreciation of hedging principles can enhance one's market acumen, contributing to more informed investment decisions and a deeper grasp of how market participants mitigate financial risks.
Examples of Hedging
In the tumultuous world of trading, a well-constructed strategy to capitalize on downtrends presents itself as a valuable hedge during periods of market volatility and uncertainty. This approach isn’t merely about safeguarding assets; it's a proactive maneuver to turn potential adversity into opportunity.
Short In Downtrend Below MA100
Consider this strategy as a kind of financial judo, where the market's downward momentum can be used to the trader's advantage. By employing techniques such as short selling, put options, or inverse ETFs, investors can not only shield their portfolios from downward spirals but also potentially profit from the negative movement of asset prices.
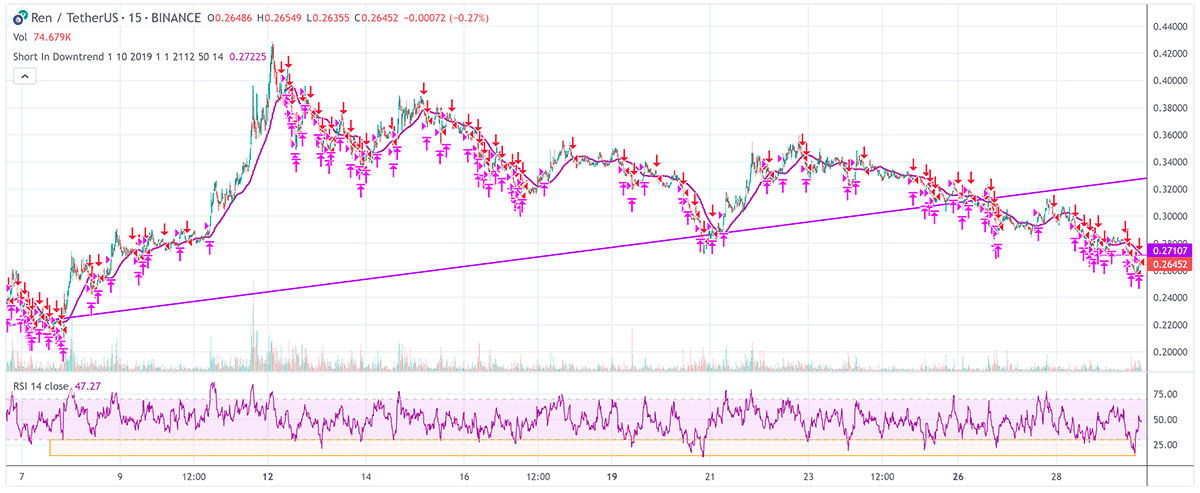
Short In Downtrend Below MA100
Short selling involves borrowing shares and selling them with the intention of buying them back later at a lower price. This move is predicated on the belief that the stock price will decline, allowing the trader to pocket the difference. Put options offer the holder the right, though not the obligation, to sell a security at a predetermined price, providing a profit if the market price falls below this level. Inverse ETFs are designed to increase in value when the price of an underlying index decreases, providing a straightforward tool for investors to gain exposure to negative market trends.
However, the use of these methods requires a nuanced understanding of market signals and risk management. Each tool comes with its inherent risks and costs. For instance, short selling exposes the trader to potentially unlimited losses if the market unexpectedly rallies. Put options can expire worthless if the anticipated decrease in price does not materialize, leading to a total loss of the premium paid. Inverse ETFs, while convenient, can suffer from tracking errors and are generally more suited for short-term hedging due to their rebalancing mechanisms.
Despite these risks, when executed with diligence and in conjunction with a comprehensive risk management plan, these strategies can offer a compelling counterbalance to long positions during bear markets or sudden downturns. They allow traders to maintain a position in the market, rather than retreating entirely, and to do so with a level of protection. It’s a strategic pivot rather than a full retreat, keeping investors engaged with the market's ebb and flow.
In essence, hedging during downtrends with these methods is an artful blend of defense and offense. It calls for a disciplined approach, an astute eye for market dynamics, and an unwavering commitment to staying informed about global economic indicators and company fundamentals. For those who master it, hedging can provide a sanctuary in stormy markets and a source of returns when others are seeing red. It's a testament to the adage that in every challenge lies opportunity, and for the astute trader, downtrends are no exception.
Regression of VX futures on the VIX
The linear regression library offers an insightful tool for traders to analyze and establish relationships between different financial instruments. In the context of hedging strategies, a pertinent example would be the regression analysis of VX futures against the VIX index. This type of analysis is vital for traders who are looking to hedge the vega exposure of their SPX options positions. To elucidate, vega represents the sensitivity of an option's price to a 1% change in the implied volatility of the underlying asset. When managing an options portfolio, it's crucial to neutralize the vega exposure to avoid significant losses due to volatility fluctuations. This is where the concept of 'beta', a measure of the volatility or systemic risk of a security or a portfolio in comparison to the market as a whole, comes into play.
In our scenario, the beta coefficient derived from the regression might signal how many VX futures one would need to hedge the vega exposure of an SPX options position. With a VX future having a beta of 0.6 to the VIX, and an SPX straddle holding a vega of 8.5, we embark on the mathematical journey to find the appropriate hedge ratio. Given the differing point multipliers – 1000 for VX futures and 100 for SPX options – it becomes clear that using the VX future as a hedge for the SPX straddle would result in an under-hedged position. Specifically, the calculation (0.6 * 1000) is less than (8.5 * 100), leaving the position with an uncovered vega of approximately 2.5, equivalent to a dollar exposure of $250.
To gauge the effectiveness of this hedge, one must turn to the R-squared value, also known as the coefficient of determination. This statistical measure reflects the proportion of variance for the dependent variable that's explained by the independent variable in the regression model. An R-squared value close to 1 indicates a robust model where VX futures are a good predictor of VIX movements. Conversely, a value significantly less than 1 would suggest a weak model and imply that the VX futures may not be the best tool for hedging the given SPX vega exposure.
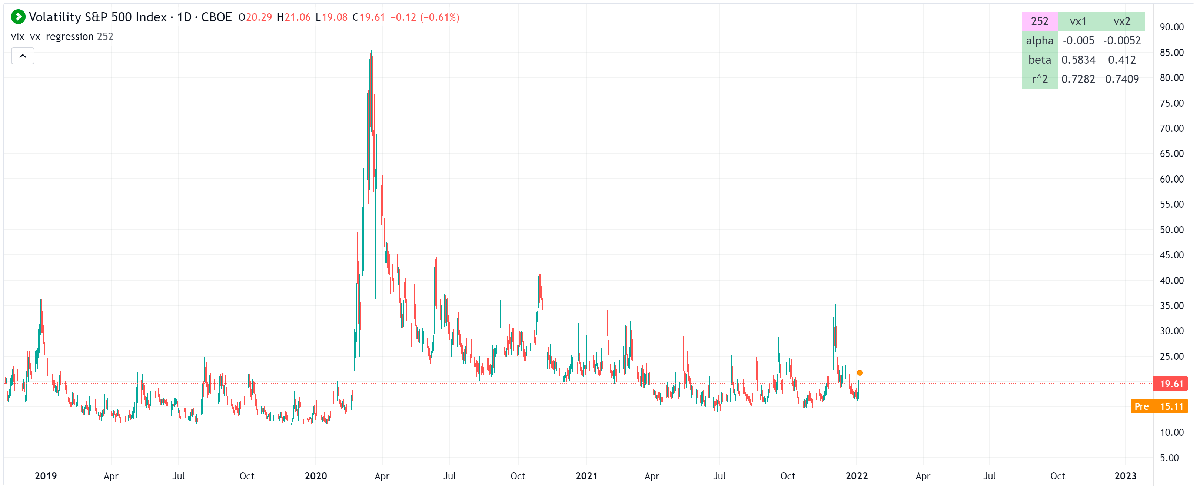
Regression of VX futures on the VIX
Furthermore, it's worth noting the presence of mini VXM futures which carry a 100 point multiplier, aligning with the SPX options. This smaller denomination offers additional flexibility in hedging strategies, particularly for traders managing smaller portfolios or those looking for more precise hedging instruments.
In conclusion, the application of linear regression in hedging strategies is more than a mere academic exercise; it's a practical approach to managing risk in a portfolio. By understanding the statistical relationship between VX futures and the VIX, and adjusting for point multipliers, a trader can design a more effective hedge against volatility exposure in SPX options. However, the strength of this relationship as determined by R-squared is a crucial factor in ensuring the hedge is both appropriate and efficient.
Market Hedge Ratio
The ratio of the market capitalization of cryptocurrencies – whether considering the total market, Bitcoin, or Ethereum – to the market cap of major stablecoins is a subtle yet telling metric in the cryptocurrency market. This ratio serves as a barometer for gauging market sentiment, providing clues on the behavior of investors at any given time.
When we talk about a low ratio, it indicates that the market cap of stablecoins is relatively high compared to the market cap of major cryptocurrencies. This could be interpreted as a sign of investor caution, with many opting to convert their holdings into stablecoins, which are pegged to less volatile assets like the US dollar, thus 'sitting in cash'. In market terms, this is akin to players being on the sidelines, ready to jump back into action if there is a favorable rally in the crypto market. This behavior suggests that there is potential for a significant market movement if those funds flow back into cryptocurrencies.
Conversely, a high ratio suggests that the market cap of cryptocurrencies is elevated relative to that of stablecoins. This condition implies that a large portion of capital is already invested in the market, which might hint at demand saturation. When most of the money has already been committed, there are fewer funds on the sidelines to drive further price increases, and the market may be overextended. This could be a precursor to a plateau or a potential retracement if investors decide to take profits, fearing that the peak has been reached.
Understanding this ratio also involves recognizing the unique role stablecoins play in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. They are a haven during periods of high volatility, allowing investors to hedge against dramatic price swings without exiting the crypto market completely. They also serve as an entry and exit ramp for cryptocurrency transactions, making them integral to liquidity within the market.
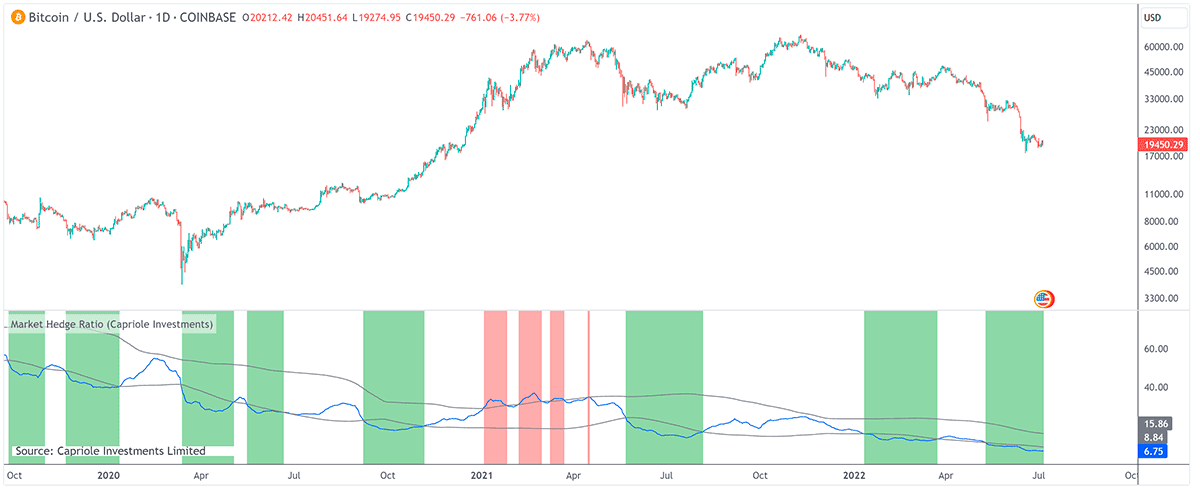
Market Hedge Ratio
However, the market cap ratio should not be viewed in isolation. Market caps can be influenced by various factors, including speculative trading and new stablecoin issuances. Moreover, the metric does not account for the distribution of stablecoins across different types of holders, which can vary widely. For instance, stablecoins held by active traders could quickly re-enter the crypto market, while those held by long-term investors might not contribute to immediate demand.
In essence, the crypto-to-stablecoin market cap ratio is a nuanced indicator that requires interpretation within the broader context of market conditions. It is an instrument that, when coupled with other indicators and market sentiment analyses, can offer strategic insights into potential market movements. However, as with all indicators, the ratio is a guide rather than a definitive predictor, and should be complemented with comprehensive market analysis to guide investment decisions.
Forex Hedging Strategies: Navigating Risks and Rewards in Currency Markets
In the intricate world of foreign exchange (Forex), hedging is akin to a finely orchestrated dance, where every step is a deliberate attempt to counterbalance potential financial missteps. The realm of Forex trading is fraught with volatility; currencies fluctuate rapidly due to a multitude of factors ranging from economic policy changes to unforeseen market events. Here, hedging strategies emerge as a pivotal element, designed to mitigate traders' exposure to unfavorable currency movements, preserving capital and stabilizing returns.
Features of Forex Hedging Strategies
Hedging in Forex involves opening multiple positions to reduce the risk exposure of an existing trade. The most common strategies include direct hedges, where traders initiate a position buying a currency pair and simultaneously sell the same pair, and complex hedges, which may involve multiple currencies or derivatives like options and futures.
A fundamental feature of hedging is leveraging derivatives – financial instruments whose value is derived from the underlying asset. Options contracts grant the buyer the right, though not the obligation, to trade a currency at a predetermined price, while futures contracts bind both parties to a set exchange rate on a future date. These instruments are central to hedging as they can be engineered to protect against price swings.
Risk Management
The cornerstone of Forex hedging is risk management. Traders utilize hedging to safeguard against unpredictable market changes that could lead to significant losses. For instance, if a U.S. investor holds significant investments in Europe, they might hedge against the risk of the euro depreciating against the dollar, which would reduce the value of their European investments when converted back to their home currency.
Advantages of Hedging
The principal advantage of hedging is reducing uncertainty and minimizing potential losses. It enables traders to secure a safety net, which can be particularly useful during times of economic instability or when significant news events are expected to prompt currency volatility. Hedging also allows investors to keep their initial positions open, potentially profiting from favorable market movements while having a backup plan should the market turn against them.
Disadvantages of Hedging
Conversely, hedging is not without its disadvantages. It requires paying premiums, particularly when dealing with options, which may eat into potential profits. Hedging can also limit gains. For instance, a perfect hedge might negate all losses but also all profits, rendering the initial trade effectively neutral. Additionally, setting up a hedge requires skill and a deep understanding of the market – a misstep can exacerbate losses rather than prevent them.
Risk Reduction vs. Cost Implication
A significant element to consider is the balance between risk reduction and the cost implication of hedging. Premium costs, the spread between bid and ask prices, and account fees all contribute to the expenses that can potentially outweigh the benefits of a hedge, especially in trades with a lower risk profile.
Hedging Strategies in Practice
Some common hedging strategies include:
- Direct Hedging: Opening an opposing position on the same currency pair.
- Multiple Currencies Hedging: Using correlations between different currency pairs to manage exposure.
- Options Hedging: Purchasing options to cover the range of potential losses on a currency pair.
- Interest Rate Hedging: Utilizing interest rate differentials between two currencies to hedge Forex exposure.
Each of these strategies serves a specific risk profile and investment horizon and demands a different level of expertise from the trader.
Complexity and the Need for Expertise
The complexity of Forex hedging is not to be underestimated. Successful hedging strategies are often the result of meticulous planning and continuous monitoring. Traders must be attuned to market dynamics, economic indicators, and geopolitical events that could affect currency valuations.
The Double-Edged Sword
Forex hedging is a double-edged sword; it can protect traders from market downturns, yet it can also prevent them from realizing potential gains. The hedging strategy chosen must align with the trader's market outlook, risk tolerance, and trading objectives.
Forex hedging is a sophisticated risk management tool, integral to the arsenal of many traders. While it provides a bulwark against market volatility, its execution requires acumen and a non-trivial assessment of costs versus benefits.
The decision to hedge should follow a comprehensive analysis of the market conditions and an individual's trading strategy, recognizing that it is as much about preserving capital as it is about forgoing potential profits. In the high-stakes dance of Forex trading, hedging can serve as the choreography that ensures traders do not misstep in the face of the market's unpredictable rhythms.
Top 10 Forex Hedging Strategies: A Blend of Prudence and Proficiency
In the world of Forex trading, hedging strategies are like the shield and spear of ancient warriors—defensive yet assertive tools designed to protect and to thrive amidst the battleground of fluctuating currencies. These strategies are critical in shaping how traders and investors navigate the inherent risks of currency movements, enabling them to weather financial storms and capitalize on market opportunities.
Forex hedging strategies involve taking strategic actions to reduce or eliminate the risk of adverse currency movements. The very essence of these tactics is not to speculate for outsized gains but to prevent potential losses. For businesses, this can mean securing procurement costs or sales revenues.
For individual traders, it can be about preserving capital or locking in profits from existing positions. The array of hedging techniques varies in complexity from straightforward spot contracts to intricate combinations of options. Each method comes with its unique blend of risk mitigation and potential cost, and the choice of strategy largely depends on the hedger's objectives, risk appetite, and market view.
Simple Forex Hedge
The simple Forex hedge involves opening a direct opposite position to a current trade. For instance, if you hold a long position on EUR/USD, you would simultaneously take a short position on the same pair. Imagine a financial tug-of-war, where any pull from currency fluctuations is countered with an equal and opposite push. The simple Forex hedge embodies this balance. It's the elemental strategy that many traders employ as a foundational defense mechanism against Forex volatility. Whether the market rises or falls, the simple hedge aims to neutralize risk, offering a cocoon of certainty within the often tumultuous trading environment.
Features:
- Direct opposite trade to an existing position.
- Quick and easy to set up.
- Does not require complex Forex knowledge.
Advantages:
- Provides immediate risk mitigation.
- Simple to understand and implement.
- Suitable for short-term protection against market fluctuations.
Disadvantages:
- Potential profits are also hedged, limiting upside gain.
- Not efficient for long-term hedging due to swap fees.
Multiple Currency Hedging
This strategy involves selecting two positively correlated currency pairs and taking opposing positions in them to offset risk. The multi-dimensional chess game of Forex hedging takes a twist with multiple currency hedging. Here, the correlation between different pairs is a strategic ally. A trader who understands the interconnected dance of currency pairs can weave a web of trades that balance each other out, capitalizing on the symphony of the Forex market's interconnected movements.
Features:
- Uses the correlation between currency pairs.
- Requires analyzing and understanding market correlations.
Advantages:
- Can hedge against a wider array of market movements.
- More dynamic and adaptable to market conditions.
Disadvantages:
- Correlations can change, introducing risk if not monitored closely.
- Requires a deeper understanding of the market dynamics.
Forex Options Trading
This involves buying options to protect against unfavorable movements in exchange rates while still allowing beneficial movements. Options are the Swiss Army knife in a trader’s toolkit—versatile and precise. By acquiring a Forex option, a trader secures the right, though not the obligation, to buy or sell at a particular price point. This strategy is akin to having a contingency plan, a calculated bet that pays off by providing flexibility and protection against adverse market gyrations.
Features:
- Grants the right, but not the obligation, to trade at a predetermined price.
- Premium paid upfront for the option contract.
Advantages:
- Flexibility to capitalize on favorable market moves.
- Defined and limited risk—the premium paid for the option.
Disadvantages:
- Premiums can be costly, reducing potential net gains.
- Complex understanding of options required.
Forex Futures Contracts
Traders use Forex futures to lock in an exchange rate for a future transaction, which can be an effective hedge against exchange rate volatility. Imagine a time machine that allows traders to freeze today's favorable exchange rates for future use. Forex futures contracts offer such a temporal anchor, a fixed rate for a future date, regardless of the tumultuous seas of market changes. They represent commitments that can insulate a financial position from the uncertainty of what tomorrow's Forex rates might bring.
Features:
- Locks in an exchange rate for a future date.
- Binding contract with legal obligation to transact.
Advantages:
- Provides certainty for future costs and revenues in foreign currencies.
- Can be tailored to specific amounts and dates.
Disadvantages:
- No benefit from favorable rate movements post-contract.
- Can be complex and may involve margin requirements.
Currency Analysis Hedging
Traders use fundamental and technical analysis to predict currency movements and enter hedges accordingly. This strategy transforms a trader into a Forex sleuth, analyzing economic reports, political news, and chart patterns to anticipate market direction. Like a detective piecing together clues, the trader uses this intel to construct hedges that are informed by a narrative of where the market could head next.
Features:
- Based on extensive market analysis.
- Adjusts hedges according to predictive insights.
Advantages:
- Hedges are informed by potentially predictive information.
- Can result in more effective hedges if analysis is correct.
Disadvantages:
- Analysis can be wrong, leading to ineffective hedges.
- Requires significant time investment and expertise.
Interest Rate Differential (IRD) Hedging
This strategy involves choosing currency pairs with different interest rates to profit from the interest rate differential. Consider the global patchwork of interest rates—an intricate mosaic that astute traders can navigate for profit. The IRD hedging strategy exploits the differences in global interest rates. By playing the long game, holding currencies with higher interest rates, and shorting those with lower rates, traders can extract value from the international tapestry of monetary policies.
Features:
- Involves holding positions to benefit from interest rate differentials.
- Requires knowledge of global interest rate trends.
Advantages:
- Potential gains from interest rate differentials.
- Can be combined with other hedging strategies.
Disadvantages:
- Interest rate fluctuations can negate the benefits.
- Requires a keen understanding of central bank policies.
Forward Contracts
Forward contracts allow traders to set a fixed exchange rate for a future date, which can be particularly useful for businesses looking to hedge future costs or revenues. Like a fortuneteller gazing into a crystal ball, forward contracts allow traders to foresee and lock in the currency rates of the future. This prescience provides a hedge against the unpredictable whims of the Forex market, ensuring that the price agreed upon today will stand firm in the days to come.
Features:
- Fixed exchange rate for future transactions.
- Contractually binding agreement.
Advantages:
- Certainty of future exchange rates.
- Customizable to specific transaction needs.
Disadvantages:
- Forgoes the advantage of future favorable rate movements.
- Not as liquid as other hedging instruments.
Natural Hedging
Natural hedging involves structuring business operations to naturally counteract currency risks, such as invoicing in the business's home currency or diversifying operations across different markets. In the forest of Forex, the natural hedge is the instinct to blend into the fiscal foliage, allowing a business to naturally camouflage itself against currency risk. Through strategic business decisions like sourcing and pricing, a company integrates risk management directly into its operational DNA.
Features:
- Invoicing in the home currency.
- Diversifying revenue and costs across different currencies.
Advantages:
- Integrates risk management into daily business operations.
- Avoids the need for complex financial hedging instruments.
Disadvantages:
- Not always possible to achieve complete natural hedging.
- May limit market opportunities due to currency considerations.
Cross-Currency Swaps
In a cross-currency swap, two parties exchange principal and interest payments in different currencies, which can be used to hedge long-term exposure. A cross-currency swap is the handshake agreement of the Forex world, where two parties agree to exchange streams of interest payments in different currencies. It's a long-term pact that serves as a bastion against exchange rate volatility, providing both predictability and potential cost savings over time.
Features:
- Exchange of interest payments and principal in different currencies.
- Long-term hedging strategy.
Advantages:
- Can lock in exchange rates for long-term obligations.
- Potential savings if interest rate differentials are favorable.
Disadvantages:
- Complex to set up and requires matching with a counterparty.
- Credit risk of the counterparty.
Option Combinations
Traders can combine various options strategies, such as straddles, strangles, and spreads, to create complex hedges that can protect against unpredictable market movements in multiple scenarios. The artistry of a master chef blending ingredients, option combinations in Forex present a gourmet of hedges—a refined mixture tailored to suit specific market outlooks. Whether it’s bracing for a major economic announcement or a period of expected turbulence, these intricate strategies serve up a dish designed for resilience and flexibility.
Features:
- Combines multiple options strategies for a tailored hedge.
- Can protect against a variety of market scenarios.
Advantages:
- Customizable to a wide range of market conditions.
- Can be structured to allow for profit in multiple outcomes.
Disadvantages:
- Often complex and difficult for beginners to execute effectively.
- Can be more expensive due to the need for multiple options contracts.
Forex hedging is a multifaceted and nuanced domain, offering traders and investors an arsenal of tools to protect their investments. While hedging can indeed act as a safeguard, the effectiveness of any strategy depends on its alignment with the trader's overall objectives, market conditions, and risk tolerance. Careful consideration and ongoing education are paramount for anyone looking to navigate the Forex market's choppy waters with hedging as their compass.
Forex hedging is a multifaceted and nuanced domain, offering traders and investors an arsenal of tools to protect their investments. While hedging can indeed act as a safeguard, the effectiveness of any strategy depends on its alignment with the trader's overall objectives, market conditions, and risk tolerance. Careful consideration and ongoing education are paramount for anyone looking to navigate the Forex market's choppy waters with hedging as their compass.
Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a newcomer to the Forex scene, understanding the varied hedging strategies is akin to a captain knowing the sails of their ship. Each approach, from the simplest hedge to the most complex option combinations, offers different levels of protection and potential profit under the ever-changing winds of market forces. The judicious use of hedging strategies not only reflects prudent risk management but also demonstrates a deep understanding of the market dynamics. It is a combination of both art and science, requiring a balanced approach and an ability to adapt to new information and market shifts. As with any financial strategy, there are no one-size-fits-all solutions, and hedging is no exception. The advantages and disadvantages of each method should be weighed against the backdrop of the market environment and the trader's individual situation.
One thing is clear, though: in the unpredictable world of Forex, hedging remains an indispensable technique for those who wish to tread carefully while pursuing their financial goals. It’s about striking the right balance between protecting one's investments and seizing opportunities that come with currency movements. In the end, the top Forex hedging strategies are those that have been customized to the user’s specific needs, carefully crafted like a tailor-made suit, offering both comfort and confidence in the face of uncertainty.
The journey of mastering Forex hedging is ongoing. As global economic landscapes shift and new financial instruments emerge, so too must hedging techniques evolve. Traders who dedicate themselves to learning and adapting these strategies will likely find that they are better equipped to manage risk and can navigate the Forex market with greater assurance and sophistication.
Top 10 Forex Brokers for Hedging in 2023
HF Markets
HF Markets stands out in the forex hedging arena by offering direct hedging capabilities on its MetaTrader platforms, which allows traders to hold multiple positions on the same currency pair in opposite directions. Their trading environment boasts tight spreads and reliable execution, complemented by a suite of tools like trading calculators and advanced charting, enhancing the hedging experience. As a multi-regulated entity, HF Markets ensures a high level of security for your trading ventures, supported by comprehensive customer service.
- Advantages: Provides tight spreads, which can be crucial for hedging strategies that require precision in entry and exit points.
- Disadvantages: Higher minimum deposit for premium accounts, which may not be suitable for all traders.
Hedging features: Allows direct hedging with no restrictions
- Hedging Capabilities: HF Markets supports direct hedging strategies on its MetaTrader platforms, allowing traders to open multiple positions in the same currency pair in opposite directions.
- Trading Environment: With tight spreads and a reliable execution policy, HF Markets ensures that traders can execute their hedging strategies efficiently and cost-effectively.
- Tools and Resources: Offers tools like trading calculators and advanced charting, which can aid in planning and executing hedging strategies.
- Regulation: Regulated by several authorities, providing a secure environment for your trading activities.
- Customer Support: Offers comprehensive customer support, an essential resource for hedgers to navigate complex situations.
Interactive Brokers
Interactive Brokers offers a robust platform tailored for sophisticated traders keen on implementing advanced hedging strategies, including forex options and futures. Its reputation for deep liquidity and institutional-grade execution aligns well with the precise needs of hedging trades. The Trader Workstation platform is a trove of features and research resources necessary for analyzing market risks, backed by rigorous regulation across multiple jurisdictions and educational materials to bolster your hedging acumen.
- Advantages: Access to a vast range of markets and instruments, including forex, options, and futures.
- Disadvantages: The complexity of the platform may be daunting for beginners.
Hedging features: Sophisticated risk management tools and the ability to create complex hedging strategies using derivatives
- Hedging Capabilities: Provides a robust platform for advanced traders looking to implement complex hedging strategies, including the use of forex options and futures.
- Trading Environment: Known for its deep liquidity pools and institutional-grade execution, which are crucial for the precise execution of hedging trades.
- Tools and Resources: The Trader Workstation platform is rich in features and research resources to analyze market risks, which is vital for hedging.
- Regulation: Highly regulated by authorities in multiple jurisdictions, ensuring a high level of trust.
- Customer Support: Offers extensive educational materials to help understand hedging and its implications.
ActivTrades
ActivTrades enables traders to employ hedging as part of its risk management palette, with competitive spreads and enhancements like SmartOrder 2 for MetaTrader. They also offer free trading tools and indicators to assist in informed decision-making. The FCA-regulated firm provides robust customer service, including one-on-one tutorials, which could be invaluable for those employing hedging strategies.
- Advantages: No commission on standard accounts and provides negative balance protection.
- Disadvantages: Limited educational resources compared to other brokers.
Hedging features: Permits hedging and offers SmartOrder 2 extension for enhanced trading functionalities
- Hedging Capabilities: Allows traders to hedge forex positions as part of its risk management features.
- Trading Environment: ActivTrades provides competitive spreads and the SmartOrder 2 extension for MetaTrader, which enhances trading functionalities including hedging.
- Tools and Resources: Offers free trading tools and indicators, including SmartForecast and SmartPattern, to assist in decision-making.
- Regulation: Regulated by the FCA, assuring a high standard of oversight.
- Customer Support: Strong customer service offering includes one-on-one tutorials which can be useful for hedgers.
FXTM
FXTM accommodates hedging through multiple trading accounts and is recognized for its swift execution times, essential for timely hedged positions. Educational resources on hedging complement their offerings, backed by a multi-jurisdictional regulatory framework and dedicated account managers for personal trading guidance.
- Advantages: Low minimum deposit requirement and fast execution speeds.
- Disadvantages: Some account types have high spreads.
Hedging features: Supports hedging and offers a variety of account types to suit different hedging strategies
- Hedging Capabilities: Supports multiple trading accounts with different strategies, including hedging.
- Trading Environment: Known for fast execution times and low latency which is key for timely hedged positions.
- Tools and Resources: Provides free educational resources that cover various aspects of hedging.
- Regulation: Regulated by multiple jurisdictions which ensures trader protection.
- Customer Support: Offers dedicated account managers for personal guidance on trading strategies such as hedging.
SaxoBank
Saxo Bank’s professional-grade platform supports complex hedging options and comes with a comprehensive toolkit for portfolio management. Its high-performance trade execution is a boon for executing intricate hedging strategies. Traders have access to expert analysis and data, crucial for hedging decisions, and premium customer support within a highly secure regulatory environment.
- Advantages: Extensive research and data analysis tools available.
- Disadvantages: Higher minimum deposit requirement, making it less accessible for small traders.
Hedging features: Offers comprehensive portfolio management and risk mitigation tools suitable for advanced hedging
- Hedging Capabilities: Offers a professional-grade platform that supports advanced hedging options with a comprehensive portfolio management toolkit.
- Trading Environment: High-performance trading with high-quality execution of trades can be particularly beneficial for intricate hedging strategies.
- Tools and Resources: Access to expert analysis and data, including detailed reports that can be crucial for hedging decisions.
- Regulation: Highly regulated by various authorities including the Danish FSA, providing a secure trading environment.
- Customer Support: Premium customer support and dedicated account managers for expert traders.
FxPro
FxPro permits hedging across multiple platforms, including MT4, MT5, and cTrader, with no dealing desk intervention to ensure unbiased execution of hedging strategies. Advanced analytical tools provided by FxPro are pivotal for enhancing decision-making, supported by stringent regulation by FCA and CySEC and comprehensive customer service.
- Advantages: No dealing desk intervention and a wide range of trading platforms (MT4, MT5, cTrader).
- Disadvantages: Charges a withdrawal fee which could impact traders moving in and out of positions frequently.
Hedging features: Allows scalping and hedging strategies
- Hedging Capabilities: Allows traders to implement hedging strategies across multiple platforms such as MT4, MT5, and cTrader.
- Trading Environment: Offers no dealing desk intervention which can ensure that hedging strategies are executed without bias.
- Tools and Resources: FxPro provides advanced analytical tools that can enhance the hedging decision-making process.
- Regulation: FxPro is well-regulated by FCA and CySEC, which enhances its reliability.
- Customer Support: Customer service includes trading support and analysis which can be helpful when implementing hedging strategies.
XM
XM embraces hedging and micro lot trading, enabling precise risk management with tight spreads and flexible leverage that are advantageous for hedging. Traders benefit from personal account managers and free market research, within a trading environment overseen by respected regulatory bodies, complemented by localized customer support in various languages.
- Advantages: Low minimum deposit and a loyalty program.
- Disadvantages: Services are not available to residents of certain countries.
Hedging features: Allows hedging and offers free VPS services, which can be beneficial for EAs running hedging strategies
- Hedging Capabilities: Permits hedging and offers the flexibility of micro lot trading, which can be particularly useful for precise risk management.
- Trading Environment: Known for tight spreads and a flexible leverage policy which can be advantageous when placing hedged trades.
- Tools and Resources: Provides personal account managers and free access to forex market research which can inform hedging decisions.
- Regulation: Regulated by the IFSC, CySEC, and ASIC, adding layers of trust for traders.
- Customer Support: Offers localised customer support in various languages which can be a boon for international traders using hedging strategies.
FOREX.com
FOREX.com offers robust hedging capabilities with integrated risk management across several platforms. Its commitment to high-quality execution and transparent pricing benefits hedging strategies, supported by a wealth of educational resources and market analysis tools, all within a securely regulated environment.
- Advantages: Wide range of currency pairs and educational resources.
- Disadvantages: Some users report a less user-friendly interface compared to other platforms.
Hedging features: Allows hedging on a variety of platforms, including Advanced Trading Platform, MT4, and MT5
- Hedging Capabilities: Offers full hedging capabilities and integrated risk management features on platforms such as Advanced Trading, MT4, and MT5.
- Trading Environment: High-quality execution and transparent pricing are key features that benefit hedging strategies.
- Tools and Resources: An extensive range of educational resources and market analysis tools are available to support hedging decisions.
- Regulation: Regulated in multiple jurisdictions including the US, UK, Canada, and Japan, offering a high level of security.
- Customer Support: Offers comprehensive customer support and trading education which can be helpful for hedgers.
Pepperstone
Pepperstone is recognized for its support of hedging on popular platforms with low spreads and non-dealing desk execution for direct market access. It provides a wealth of smart trading tools and educational content essential for sophisticated hedging strategies, within a trading framework regulated by top-tier financial authorities, and is known for its award-winning customer support.
- Advantages: No dealing desk execution and supports a range of third-party platforms like TradingView
- Disadvantages: Limited proprietary research and analysis.
Hedging features: Allows hedging and offers ultra-low spreads
- Hedging Capabilities: Supports hedging on MT4, MT5, and cTrader with some of the industry's lowest spreads.
- Trading Environment: Non-dealing desk execution means traders receive direct market access, essential for timely and accurate hedging.
- Tools and Resources: Offers smart trader tools and a rich array of educational content for developing sophisticated hedging techniques.
- Regulation: Regulated by ASIC and FCA, ensuring adherence to strict financial standards.
- Customer Support: Provides award-winning customer support that is responsive and helpful for complex strategies.
Oanda
Oanda facilitates hedging through a user-friendly platform equipped with advanced charting and analysis tools. Its strong regulatory oversight and transparent pricing provide a dependable trading environment for risk management. The provision of advanced analytical tools and historical data is a significant asset for planning hedges, rounded out by robust educational and customer support services.
- Advantages: User-friendly platform and transparent pricing.
- Disadvantages: Their range of products is more limited compared to other major brokers.
Hedging features: Supports hedging and provides a powerful trading engine
- Hedging Capabilities: Facilitates hedging on a user-friendly platform with advanced charting and analysis tools.
- Trading Environment: Oanda's trading performance is backed by strong regulatory oversight and transparent pricing, which is essential for risk management in hedging.
- Tools and Resources: Provides advanced analytical tools and access to historical exchange rate data which can be very useful when planning hedges.
- Regulation: Well-regulated by top-tier authorities, including the CFTC and FCA, offering traders peace of mind.
- Customer Support: Offers robust customer service, including educational materials that are particularly useful for understanding and applying hedging techniques.
Each of these brokers has been chosen based on their ability to provide a robust platform for hedging within forex trading, taking into account the cost of trading, platform stability, regulatory oversight, and the ability to execute complex trading strategies. It's essential for traders to further investigate each broker to ensure that it fits their individual trading style and hedging requirements. Keep in mind that hedging can protect against losses but also limit potential profits, and it requires a good understanding of market dynamics.
Each broker provides a unique blend of tools, resources, and services that can significantly influence the efficacy of forex hedging strategies. Traders should consider these attributes in relation to their individual needs and preferences to select the broker that best facilitates their hedging approach.
In conclusion, these brokers provide a range of features that cater to the needs of traders looking to implement hedging strategies in the forex market. It’s important for traders to evaluate these overviews in light of their specific needs, trading style, and risk tolerance before deciding on the broker that best fits their hedging strategy.
Navigating Currency Risks: Top 10 Expert Advisors for Forex Hedging Mastery
In the fluid dance of the Forex market, where currency values fluctuate with the pulse of global events, traders seek stability in the midst of chaos. Hedging, a strategy as old as markets themselves, has found a new lease on life through the digital genius of Expert Advisors (EAs). These algorithmic sentinels, tailored for MetaTrader platforms, are revolutionizing how traders mitigate risk, offering a shield against the unpredictability of exchange rates. This article delves into the top 10 EAs designed for those who wish to refine their hedging tactics—each a beacon of calculated foresight amidst the unpredictable seas of Forex trading.
Enhance Your Trading Arsenal with Advanced EAs Tailored for Hedging Strategies
In the world of Forex trading, hedging stands as a strategic bulwark against the unpredictability of currency markets. It's a technique akin to taking out an insurance policy; while it might not reap profits, it provides a measure of financial security during turbulent economic weathers. Integral to modern trading, Expert Advisors (EAs)—algorithmic bots designed for the MetaTrader platform—have emerged as vital tools for implementing complex hedging strategies. These sophisticated software systems can automatically execute trades based on predefined criteria, enabling traders to manage risks around the clock with greater precision and discipline than manual trading often allows.
Here are the top 10 Forex Expert Advisors crafted for optimizing hedging strategies:
The Guardian Angel EA
The Guardian Angel EA serves as a vigilant protector of investments. It prides itself on a conservative approach, placing small, incremental trades across various currency pairs to distribute risk.
- Features: Multi-currency hedging, automatic stop-loss settings, user-defined risk levels.
- Advantages: Limits exposure effectively, intuitive user interface, good for beginners.
- Disadvantages: May generate lower profits due to conservative trading, limited to certain currency pairs.
The Arbitrage Wizard EA
As the name suggests, this EA seeks to exploit pricing inefficiencies between pairs, thereby employing a sophisticated form of hedging.
- Features: Real-time arbitrage opportunities, simultaneous multi-pair monitoring, rapid execution.
- Advantages: High-frequency trading can lead to quick, albeit small, gains; relatively low-risk strategy.
- Disadvantages: Requires a fast and reliable connection, may be subject to broker limitations on arbitrage trading.
The Volatility Fighter EA
This EA is designed to thrive in volatile markets, using hedging to safeguard against sudden price swings.
- Features: Volatility detection, automatic hedging based on user-defined thresholds, and diverse trading instruments.
- Advantages: Performs well in unstable market conditions, robust risk management tools.
- Disadvantages: May require more sophisticated understanding to configure, potential for high drawdown during extreme volatility.
The Trend Watcher EA
Hedging with this EA is based on the detection of long-term market trends, taking counter-positions as a defensive strategy.
- Features: Trend analysis algorithms, backward and forward-testing capabilities, stress-tested scenarios.
- Advantages: Benefits from sustained market movements, historical data-driven decision making.
- Disadvantages: Can be slow to react to short-term market reversals, trend dependency.
The Swap Master EA
Swap Master takes a unique approach by exploiting differences in broker interest rates or swaps through hedging techniques.
- Features: Swap rate analysis, cross-broker hedging, automatic trade adjustments.
- Advantages: Can generate profits from swaps as well as price movements, minimal market exposure.
- Disadvantages: Swap rates must be carefully monitored, strategy may not be suitable for all brokers.
The Equilibrium EA
Focused on achieving balance, the Equilibrium EA uses hedging to maintain a stable equity curve.
- Features: Equity control mechanism, proportional hedging based on account size, automated risk management.
- Advantages: Steady growth potential, decreased likelihood of large drawdowns.
- Disadvantages: Growth may be slower compared to more aggressive EAs, potential underperformance in trending markets.
The Risk Allocator EA
This EA allocates risk across multiple pairs and strategies, using hedging as a way to offset losses in any single trading strategy.
- Features: Multi-strategy trading, automatic pair selection, and integrated risk assessment.
- Advantages: Diversification of risk, adaptive to various market conditions.
- Disadvantages: Complex setup for inexperienced traders, requires constant tuning.
The Hedge Grid EA
Hedge Grid uses a grid strategy with hedging to capitalize on natural market movements.
- Features: Grid-based trading, automatic lot sizing, hedging on each grid level.
- Advantages: Can profit from market range conditions, predefined entry and exit points.
- Disadvantages: Grid strategies can involve significant risk if not properly managed, not ideal for trending markets.
The Currency Protector EA
This EA focuses on protecting currency investments by hedging against potential losses in specific currency pairs.
- Features: Specific pair targeting, loss prevention tactics, strategic exit planning.
- Advantages: High customization for individual pairs, clear strategy for loss mitigation.
- Disadvantages: May miss broader market opportunities, requires in-depth knowledge of the targeted currency pair.
The Correlation Chief EA
It capitalizes on the correlation between currency pairs, establishing hedges when those relationships deviate.
- Features: Correlation analysis, automated hedge execution, real-time adjustment to correlation shifts.
- Advantages: Innovative use of currency correlations, dynamic adjustment to market conditions.
- Disadvantages: Requires understanding of complex market correlations, high-level strategic planning.
Each of these EAs presents a unique avenue through which traders can employ hedging strategies to mitigate risk. It's essential, however, for traders to understand that while EAs automate trades, they don't replace the nuanced judgment and ongoing vigilance required for successful Forex trading. Moreover, the effectiveness of an EA is contingent upon the quality of its algorithm, the conditions of the market, and the compatibility with the trader's personal strategy and risk tolerance. Therefore, thorough testing and a deep dive into individual features and operational specifics are recommended before deploying any EA in a live trading environment.
Related Materials
Navigating the intricacies of forex trading can often feel like navigating a labyrinth for beginners. The key to unlocking success within this maze lies in equipping oneself with robust forex trading strategies and techniques. As you venture into the world's largest financial market, having a reliable roadmap in the form of a trading strategy can be a game-changer.
Forex trading, with its high liquidity and rapid price movements, offers traders numerous opportunities. However, it is crucial to have the right strategy to harness these opportunities effectively. Here, we explore the top 5 most profitable forex trading strategies, delving into their advantages and disadvantages...
The anatomy of swing forex trading is deeply rooted in technical analysis. Forex swing traders employ a myriad of tools candlestick patterns, moving averages, momentum indicators like the RSI or MACD, and Fibonacci retracement levels to decipher potential entry and exit points.
Scalping is a popular and fast-paced trading strategy used primarily in the Forex market. The primary objective for scalpers is to capture small price movements with the intention of securing quick profits...
The Trend Following strategy is a widely practiced approach in the world of Forex trading. At its core, the philosophy behind it is simple: Markets tend to move in trends, and the goal is to capture profits from these movements. Traders adopting this strategy will aim to enter the market in the direction of the prevailing trend, seeking to ride the momentum for as long as the trend lasts.
In the vast tapestry of Forex trading methodologies, position trading occupies a distinct niche. Rather than riding the short-term waves and troughs, position traders set their sights on the long-term, capitalizing on extended market movements...
Breakout Trading Strategy capitalizes on moments when an asset breaks beyond established resistance or support levels. This movement could signal the start of significant price movements, and traders aim to enter the market right as the breakout happens, hoping to profit from the subsequent trend...
Trusted Forex Brokers
| Broker | Review | Rating | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HF Markets | ||
| 2 | NordFX | ||
| 3 | Octa | ||
| 4 | FXCM | ||
| 5 | Interactive Brokers | ||
| 6 | ActivTrades | ||
| 7 | FXTM | ||
| 8 | easyMarkets | ||
| 9 | HYCM | ||
| 10 | SaxoBank | ||
| 11 | FxPro | ||
| 12 | Moneta Markets | ||
| 13 | XM | ||
| 14 | FOREX.com | ||
| 15 | Admirals | ||
| 16 | eToro | ||
| 17 | FIBO Group | ||
| 18 | Pepperstone | ||
| 19 | PrimeXBT | ||
| 20 | IronFX | ||
| 21 | Forex4you | ||
| 22 | InstaForex | ||
| 23 | INGOT Brokers | ||
| 24 | Swissquote Bank | ||
| 25 | Oanda |